Blockchain is gaining extreme popularity and is probably considered among the greatest invention since the internet itself. Everyone has heard about it but not anyone knows about it.
Blockchain helps in value exchange without the presence of any central authority and the need for trust. Blockchain technology can be considered as secure, quick and cheap. Blockchain is the technology that runs Bitcoin.
Brief History
The primitive form of the blockchain was the hash tree originally patented by Ralph Merkle, its main function was to handle the data between the computer systems.
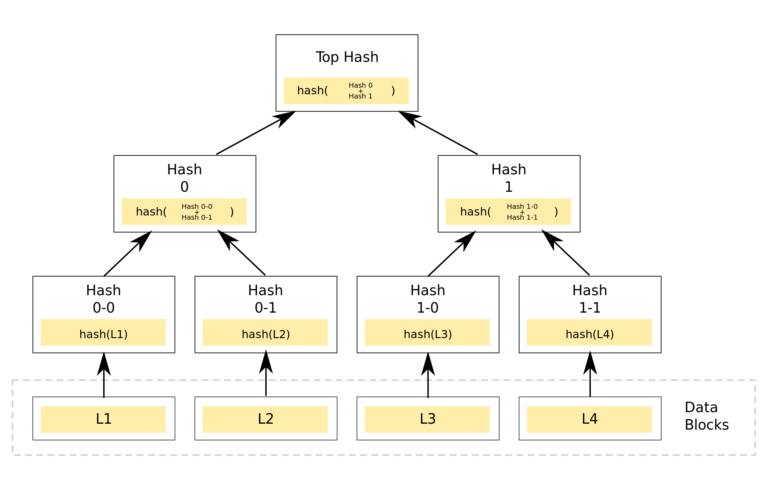
In the peer-to-peer network connection, validating the data is the most important phase so as to ensure that nothing was altered during the process of transfer. Its main essence is to maintain the integrity of the data.
In 1991, the hash tree was used to create a secured chain of blocks. It basically constitutes the data records each connected to one after it. The newest formed record contains the history of the entire chain. And thus, the blockchain was created.
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto conceptualized the distributed blockchain. It was a peer-to-peer network with all the verified data exchanges and could be managed autonomously without any human interference. Thus, this technology became the backbone of the Bitcoin. And thus blockchain was born and the number of digital cryptocurrencies.
Working
Let’s learn how the blockchain technology works by taking an example of its most popular application i.e. Bitcoin. Bitcoin is the digital currency that has gained extreme popularity over the past year and is used to exchange products or services. The Bitcoin-only has the value because we accept it for trading, which makes the currency under control, and we believe that others will do the same. The amount of the bitcoins owned by an individual is tracked by the blockchain which uses the ledger, a digital file that tracks all the transactions.
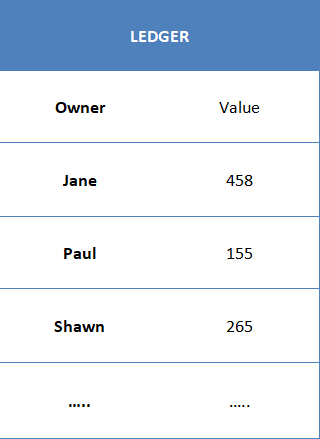
The ledger doesn’t belong to a single entity server like a bank or a particular data center. It is distributed across all the private computers that store the data and execute the computations. Each private computer in the blockchain network is known as a “node” which contains a copy of a ledger file.
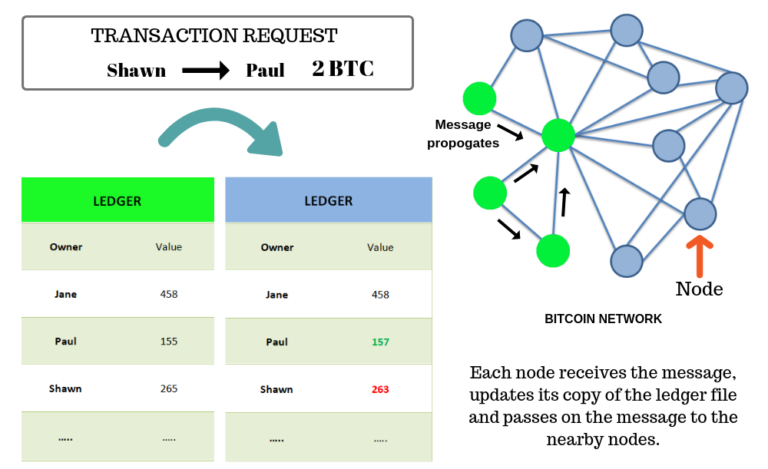
Let’s consider an example; if Shawn wants to transfer 2 BTC to Paul when he broadcasts the message to the network which resembles loss of 2 BTC from Shawn’s account and gaining of 2 BTC into Paul’s account. While the message is getting transferred each node will copy information about the requested transaction to its copy of the ledger file, thereby updating the account balances. During the transfer, the transaction request message is copied to each ledger file contained by each node, which results in updating the account balances.
In order to perform the transactions on the blockchain, you need a bitcoin wallet that stores and exchanges the bitcoins. The bitcoin wallet is protected by the unique pair of public and private keys using the cryptographic method.
The functionality of these keys is like if you encrypt the message using your public key then only the one who owns the paired private key can decrypt and read the message. When Shawn wants to send the bitcoins, he needs to encrypt the message with his private key; hence he is the only one who can spend bitcoins. Each node is verified to check whether the transaction request is coming from Shawn by decrypting the message with his public key.
While encrypting a particular transaction with your wallet’s private key, a digital signature is generated which is used by the blockchain computers for the verification of the source and its authenticity. A digital signature is a string of text, which is the combination of a transaction request message and a private key owned by the individual, which is unique and cannot be used for other transactions.
Even a single character change in the transaction request message will change the digital signature, so there are no chances of changing the requests or altering the amount of bitcoin that you send.
To send the bitcoin you need to prove that you are the one who owns the private key of the wallet as it is needed to encrypt your transaction request message. Once the message has been broadcasted after encryption, you don’t have to worry about your private key.
As we have got the basic understanding of how the blockchain works, let’s consider some benefits of it –
Benefits of Blockchain
- The cost to perform the transaction is very low which allows micropayments.
- The transaction can be performed within minutes and can be considered as secure after a few hours.
- Verification of every transaction is made on the blockchain, which results in full transparency and increased security.
- The owner of the wallet has the whole control over it, there is no third party involved that holds your value or limits your access.
Overall, blockchain technology is huge and quite complex when we dig into creating one, but it has the potential to revolutionize many industries. Its main advantage lies in its decentralized nature and ability to eliminate the trust factor. Many cryptocurrencies are being developed to improve the blockchain security and its wider range of features.